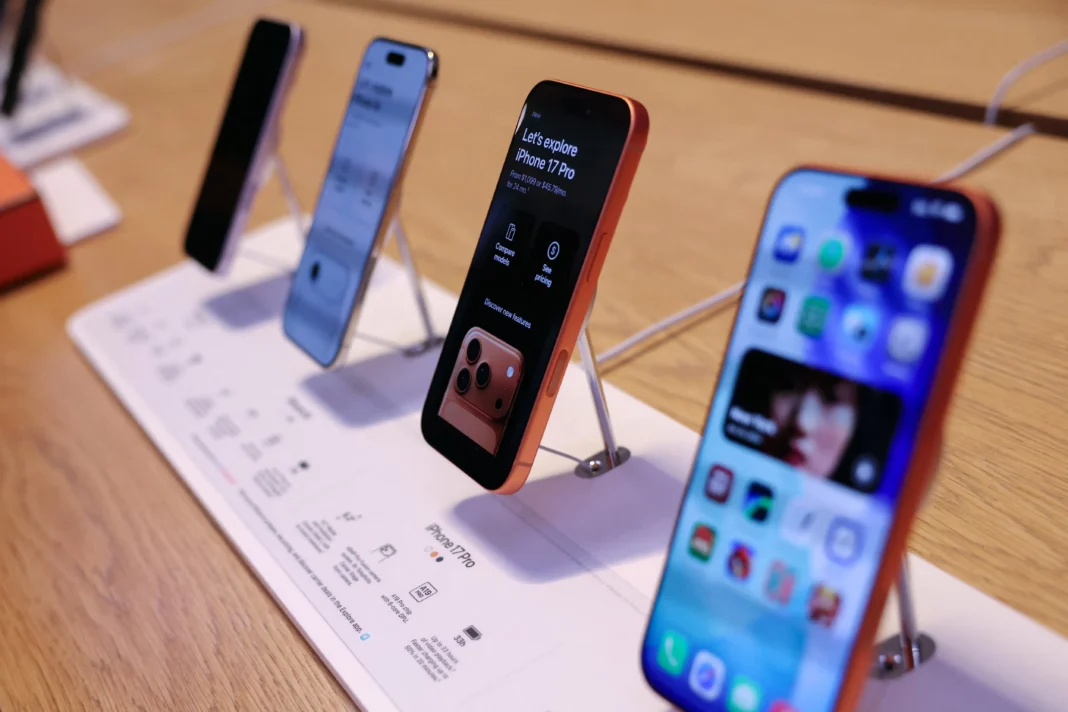
PARIS — In the sleek corridors of the Apple Store at Marché Saint-Germain, the usual buzz of tech enthusiasts now carries an undercurrent of economic tension. As the 2026 global memory chip crunch intensifies, the tech world is fixated on a singular, high-stakes gamble: Will Apple protect its margins through price hikes, or will it weaponize the crisis to capture a larger slice of the European market?
The Silicon Squeeze: Why Your Next Upgrade May Cost More
The current shortage of Dynamic Random Access Memory (DRAM) is not merely a supply chain hiccup; it is a structural byproduct of the artificial intelligence revolution. Global tech titans—Meta, Google, and Microsoft—are aggressively building out AI infrastructure, absorbing vast quantities of memory chips for high-margin data centers. This has left consumer electronics manufacturers fighting for the remnants, with chip prices predicted to rise sharply throughout the year.
For the French consumer, the implications are stark. Analysts suggest that while Apple possesses the fiscal “clout” to secure supply from giants like Samsung and SK Hynix, its rivals—particularly smaller Android manufacturers—are already feeling the squeeze.
Apple’s Strategic Dilemma
During a recent post-earnings call, CEO Tim Cook acknowledged the sharp rise in component costs but remained characteristically elusive regarding pricing. “There are different levers that we can push,” Cook noted, leaving the door open for several scenarios:
- The Market-Share Offensive: If Apple maintains current pricing while competitors are forced to raise theirs, the iPhone 17 becomes a significantly more attractive value proposition in the premium segment.
- The Profit-Margin Defense: Should Apple choose to hike prices, it would signal a prioritize-profit strategy, potentially giving rivals the “ceiling” they need to follow suit.
Industry veterans suggest that Android makers are “cautiously watching” Cupertino’s next move. If Apple absorbs the cost increase, Android devices—which lack Apple’s vertical integration and purchasing power—could suddenly look overpriced by comparison.
The European Perspective: The “French Angle”
In France, where the iPhone 17 (256GB) currently retails for approximately €969, the debate over pricing is further complicated by the European Union’s regulatory landscape. The Digital Markets Act (DMA) has already forced Apple to open its ecosystem to third-party app stores and alternative payment methods within the EU.
This regulatory pressure, combined with the chip shortage, creates a unique “Brussels Effect.” While Apple might be tempted to raise prices to offset the loss of App Store commissions in Europe, doing so during a supply crisis could alienate a consumer base already weary of the “premiumization” of essential tech. Furthermore, with global smartphone shipments projected to decline for the first time since 2023, the French market represents a critical battleground for maintaining long-term loyalty.
Takeaways
- AI Infrastructure Drain: The rapid expansion of AI data centers is diverting memory chips away from smartphones, driving up costs.
- Supply Dominance: Apple’s long-standing relationships with suppliers like Samsung and Micron may allow it to bypass the supply constraints crippling smaller firms.
- Investor Tension: Holding prices could boost market share but risk “upsetting” investors concerned with profit margins.
- A “Two-Horse Race”: Apple and Samsung are uniquely positioned to absorb these costs, potentially tightening their grip on a shrinking global market.